This website stores cookies on your computer.
These cookies are used to collect information about how you interact with our website and allow us to remember you. We use this information in order to improve and customize your browsing experience and for analytics and metrics about our visitors both on this website and other media. To find out more about the cookies we use, see our Privacy Policy.
Transforming Devices at the Edge
The Next Evolution of Compute with Embedded AI
Artificial intelligence is changing how computing happens. It is no longer limited to the cloud or large data centers. Today, intelligence is moving closer to where data is created. From factory machines and hospital equipment to retail cameras and delivery vehicles, devices are beginning to process information and make decisions on their own.
This change is powered by embedded AI, which integrates artificial intelligence directly into hardware components such as CPUs, GPUs, and NPUs. Instead of sending data to a distant cloud for analysis, these chips can process it locally. The result is faster insight, improved privacy, and less dependence on network connections.
As data volumes continue to rise, traditional cloud-only architectures are reaching their limits. According to Statista, there will be more than 29 billion connected devices by 2030, producing massive amounts of information that cannot all be processed centrally. Local intelligence helps organizations act on data immediately and only send what is necessary to the cloud. This approach supports real-time decision-making while improving security, energy efficiency, and sustainability.
This change is powered by embedded AI, which integrates artificial intelligence directly into hardware components such as CPUs, GPUs, and NPUs. Instead of sending data to a distant cloud for analysis, these chips can process it locally. The result is faster insight, improved privacy, and less dependence on network connections.
As data volumes continue to rise, traditional cloud-only architectures are reaching their limits. According to Statista, there will be more than 29 billion connected devices by 2030, producing massive amounts of information that cannot all be processed centrally. Local intelligence helps organizations act on data immediately and only send what is necessary to the cloud. This approach supports real-time decision-making while improving security, energy efficiency, and sustainability.

We are seeing the next phase in computing:
Embedded AI transforms how organizations use data. It improves responsiveness, enhances privacy, reduces energy use, and controls costs—all while making systems smarter and more resilient.

Embedded AI changes how devices compute and communicate. In traditional systems, data was sent to central servers for processing. Embedded AI brings the same intelligence directly to the device.
- Cloud-first AI brought scale and accessibility.
- Hybrid AI balanced workloads between cloud and on-premises environments.
- Embedded AI now adds intelligence directly to the device.
Advantages of Embedded AI
Embedded AI transforms how organizations use data. It improves responsiveness, enhances privacy, reduces energy use, and controls costs—all while making systems smarter and more resilient. Latency and Performance
Local processing means faster action. A camera on a production line can detect a defect as it happens. A hospital monitor can flag an irregular heartbeat immediately. An autonomous vehicle can adjust its course in real time. Eliminating round trips to the cloud delivers the speed needed for safety, efficiency, and precision.Data Privacy and Security
When information stays on the device, exposure risks are reduced. Healthcare, finance, and government organizations can analyze data locally while protecting personal details. This helps meet compliance standards such as HIPAA, GDPR, and FedRAMP. Local processing also limits the number of systems handling sensitive data, reducing the attack surface.Energy Efficiency
Moving and processing large amounts of data consumes significant energy. Embedded AI lowers this footprint by performing analysis within purpose-built chips designed for efficient inference. For mobile or remote operations, like agriculture sensors or renewable energy systems, this efficiency directly supports sustainability goals.Cost Optimization
Cloud resources are valuable but can be expensive when used for every task. By handling inference locally, organizations reduce bandwidth and cloud compute costs while freeing the cloud for model training or analytics. The result is a balanced, cost-efficient strategy that scales smoothly.Strategic Business Impact
Embedded AI does more than improve technical performance. It accelerates innovation by enabling new services, improves reliability through real-time decisions, and increases return on investment by lowering operating costs. When systems learn and adapt at the edge, organizations gain both speed and agility.Embedded AI delivers faster, smarter performance

How Embedded AI Works: A New Architecture for Edge Intelligence
Embedded AI changes how devices compute and communicate. In traditional systems, data was sent to central servers for processing. Embedded AI brings the same intelligence directly to the device.A Collaborative Compute Model
Modern processors use several specialized parts that work together:- CPUs (central processing units) handle coordination and general operations.
- GPUs (graphics processing units) process visual and data-intensive workloads in parallel.
- NPUs (neural processing units) perform AI inference efficiently using minimal power.

Software and Model Deployment
AI models are typically trained in the cloud, where large datasets and resources are available. Once trained, they are compressed and optimized for deployment to edge devices. Frameworks such as TensorRT, ONNX, or OpenVINO help translate models so they run efficiently on different hardware. Updates can then be distributed through secure, centralized management tools.Management and Monitoring
IT teams can monitor performance, update models, and enforce security policies across thousands of devices from a single interface. This level of visibility ensures consistent performance and makes it easier to maintain compliance across distributed operations.Innovation in the Hardware Ecosystem
Leading manufacturers are building AI capabilities directly into their processors:- Intel® Core™ Ultra and Xeon® processors integrate AI acceleration for high-speed inference.
- NVIDIA Jetson and RTX platforms provide GPU power for robotics, vision systems, and automation.
- AMD Ryzen™ AI and EPYC™ processors improve performance for distributed and compute-heavy workloads.
The Device-to-cloud Continuum
Embedded AI complements, rather than replaces, cloud computing. Devices handle immediate decisions, edge servers coordinate multiple systems, and the cloud manages storage, model training, and analytics. Together, they form a flexible, distributed intelligence model that strengthens performance and resilience.
Embedded AI Across Industries
Embedded AI is already transforming operations across industries that depend on timely insight and reliable automation.
Manufacturing
Factories are using embedded AI to improve output, safety, and predictive maintenance.
- Predictive maintenance: Machines monitor vibration and temperature data to detect issues before failure.
- Automated inspection: Vision systems identify defects in real time, reducing waste and rework.
- Safety monitoring: Sensors detect unsafe conditions and shut down equipment automatically.
Healthcare
In healthcare, embedded AI supports faster diagnosis and better patient monitoring.
- AI-assisted imaging can analyze scans locally and flag potential issues in seconds.
- Connected monitoring devices continuously analyze patient data for early warning signs.
- Portable diagnostic tools use local AI processing for accurate, on-the-spot results.
Retail and Logistics
Retailers and logistics companies are adopting embedded AI to streamline operations.
- Smart cameras track shelf inventory and customer movement in real time.
- Autonomous checkout systems identify items instantly, improving convenience.
- Fleet management tools optimize delivery routes and vehicle maintenance.
Energy and Utilities
Embedded AI is helping utilities manage complex, distributed infrastructure. Smart sensors in energy grids or pipelines detect anomalies and predict maintenance needs, reducing outages and improving safety. Edge AI can also balance power usage dynamically, supporting renewable energy sources and sustainability goals.
Transportation
Connected vehicles and city traffic systems rely on embedded AI for real-time decision-making. Cameras and sensors process video locally to detect hazards, manage traffic flow, and improve safety. This local processing reduces network strain and enhances reliability, even in areas with poor connectivity.
When milliseconds matter, embedded AI ensures intelligence is right where the action happens.
Getting Started: Building Your Embedded AI Strategy
Adopting embedded AI requires a clear plan that aligns with both technology and business goals. The following six steps can help guide the process.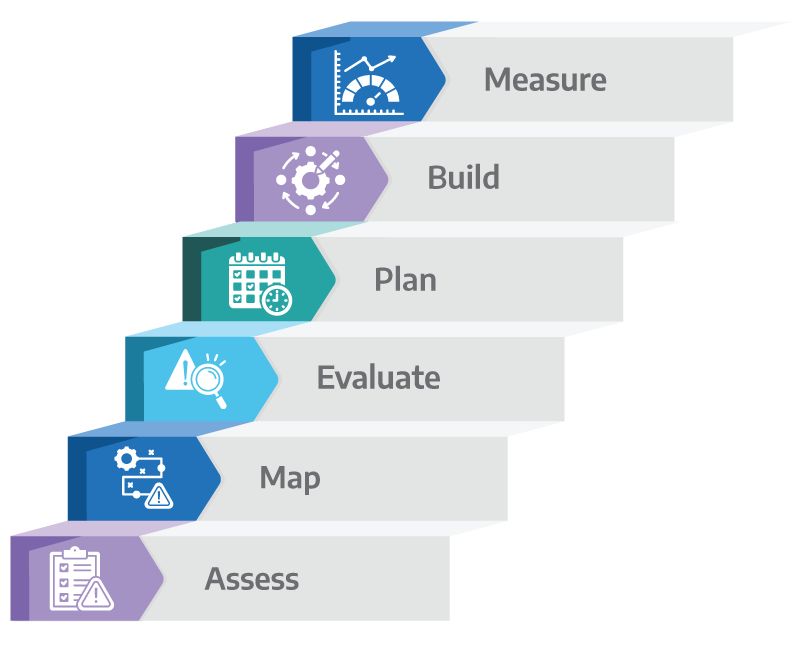
Step 1: Assess Edge Workloads
Identify applications that rely on rapid decision-making, such as predictive maintenance, imaging, or sensor analytics. These areas often deliver the fastest return.
Step 2: Map Data Sensitivity
Decide what data must remain local for compliance or security reasons. Embedded AI can process and anonymize sensitive data before sending summaries to the cloud.
Step 3: Evaluate Hardware Readiness
Review your current devices and systems to see which already include AI acceleration. Many processors have built-in capabilities that can be activated with software upgrades.
Step 4: Plan for Integration
Design a hybrid architecture that connects embedded systems with cloud analytics for unified visibility. Ensure security and governance policies are consistent across all layers.
Step 5: Build Skills and Partnerships
Work with experienced partners to fill knowledge gaps and accelerate deployment. Training IT teams to manage AI workloads at the edge ensures sustainable growth.
Step 6: Measure and Scale
Use performance metrics such as latency, uptime, and cost savings to measure results. Successful pilots can then be scaled to additional devices or sites.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
✘ Deploying devices without clear integration plans.
✘ Ignoring data governance and update management.
✘ Underestimating the need for staff training and support.
According to International Data Corporation (IDC), spending on edge computing infrastructure is expected to grow at a double-digit compound annual growth rate through 2028.
Empowering the Device-to-cloud Ecosystem
Connection helps organizations design and deploy AI-ready infrastructure from endpoint to cloud. Through partnerships with organizations such as Intel, Dell, and Lenovo, Connection provides access to devices and solutions optimized for embedded AI performance, energy efficiency, and security. By integrating intelligence directly into devices, organizations can make faster decisions, strengthen privacy, and reduce costs. Connection helps customers build the foundation for this transformation with the right hardware, expertise, and long-term support.
Streamlining the Edge: Infrastructure Management at Scale
Set your team up for success in highly distributed edge environments. This article will uncover strategies for accelerating the deployment of distributed edge infrastructures at scale, including how to enable observability into server health and configuration and to automate device discovery, inventory, tracking, monitoring, and updates.
- DevOps and IT Operations in Edge Management
- DevEdgeOps: A Unified Approach
- Key Features for Edge Infrastructure Management
- Accelerating Edge Deployments at Scale
- DevEdgeOps in Action
Edge Infrastructure Unlocks Innovation
Edge computing architectures can dramatically improve the performance of highly distributed business-critical applications, enabling innovation. Edge computing moves processing to the edge of the enterprise network where it is closest to users and devices—and, most critically, where the data that must be processed is generated.